The human body is a complex network of organs, each with its own unique role in maintaining health and equilibrium. Among these, the digestive gland stands as a vital but often overlooked organ.the pancreas, which is located deep within the abdomen, is essential for both blood sugar management and digesting.In this article, we delve into the intricacies of the digestive gland exploring its structure, function, and significance in maintaining overall well-being.
Understanding the Pancreas:
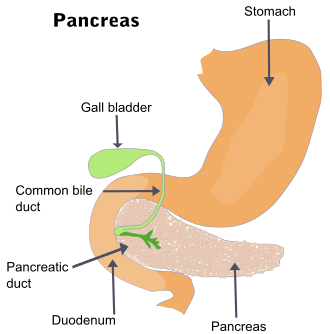
The pancreas is a long, slender organ located behind the stomach, stretching horizontally across the abdomen. Despite its relatively inconspicuous appearance, the pancreas is indispensable to human survival. Structurally, it comprises two main functional components: the exocrine pancreas and the endocrine pancreas.
Exocrine Function:
The exocrine digestive glandprimarily produces digestive enzymes and bicarbonate, essential for breaking down food in the small intestine. These enzymes, including amylase, lipase, and proteases, facilitate the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, respectively. Additionally, bicarbonate helps neutralize the acidic chyme entering the small intestine from the stomach, creating an optimal pH environment for enzymatic activity.
Endocrine Function:
Contrary to its exocrine counterpart, the endocrine digestive gland regulates blood sugar levels by secreting hormones into the bloodstream. The key players in this regulatory process are insulin and glucagon, synthesized by specialized cells known as beta cells and alpha cells, respectively. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, thereby lowering blood sugar levels, while glucagon acts in opposition, stimulating the release of glucose from glycogen stores when blood sugar levels dip too low.
Dynamic Regulation of Blood Sugar:
Maintaining blood sugar within a narrow range is crucial for sustaining energy levels and overall metabolic health. The pancreas orchestrates this intricate balancing act through a finely tuned feedback mechanism. After a meal, when blood sugar levels rise, beta cells in the pancreas secrete insulin, promoting the uptake of glucose by cells for energy production and storage. Conversely, during periods of fasting or heightened energy demand, alpha cells release glucagon, prompting the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream.
Disruptions in Pancreatic Function:
Any imbalance in pancreatic function can have profound implications for health. Conditions such as diabetes mellitus exemplify the repercussions of dysfunctional pancreatic regulation. In type 1 diabetes, the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys beta cells, leading to insulin deficiency and uncontrolled blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, arises from a combination of insulin resistance and impaired insulin secretion, often stemming from lifestyle factors such as obesity and sedentary behavior.
Beyond Diabetes:
While diabetes is perhaps the most well-known consequence of pancreatic dysfunction, the implications extend far beyond this singular condition. Pancreatitis, characterized by inflammation of the pancreas, can result from various factors, including gallstones, alcohol abuse, or certain medications. Acute pancreatitis manifests as sudden and severe abdominal pain, often necessitating hospitalization, while chronic pancreatitis entails persistent inflammation and irreversible damage to pancreatic tissue.
Pancreatic Cancer:
Another formidable challenge associated with the digestive gland is pancreatic cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to nonspecific symptoms and rapid progression. With a notoriously low survival rate, pancreatic cancer poses a significant public health concern. Research efforts are underway to elucidate its underlying mechanisms and develop more effective treatment modalities, but formidable obstacles remain.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pancreas occupies a central role in human physiology, governing both digestion and blood sugar regulation. Its intricate interplay with various hormones and enzymes underscores its indispensability to overall health and well-being. From facilitating nutrient absorption to fine-tuning blood sugar levels, the pancreas quietly orchestrates a symphony of metabolic processes essential for sustaining life. As our understanding of its complexities deepens, so too does our appreciation for this unassuming yet indispensable organ.

