The viginal health, often shrouded in mystery and misconceptions, is a crucial component of the female reproductive system. Far from being a simple passageway, the vagina is a complex and dynamic organ that plays a pivotal role in sexual pleasure, childbirth, and overall vulva health. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the intricacies of vaginal anatomy, exploring its structure, functions, and the importance of viginal health.
Understanding viginal health and Structure:
Viginal health mean the vagina is a muscular canal that extends from the vulva (external genitalia) to the cervix (the lower part of the uterus). Despite its relatively small size, the vagina consists of multiple layers and structures that contribute to its form and function.
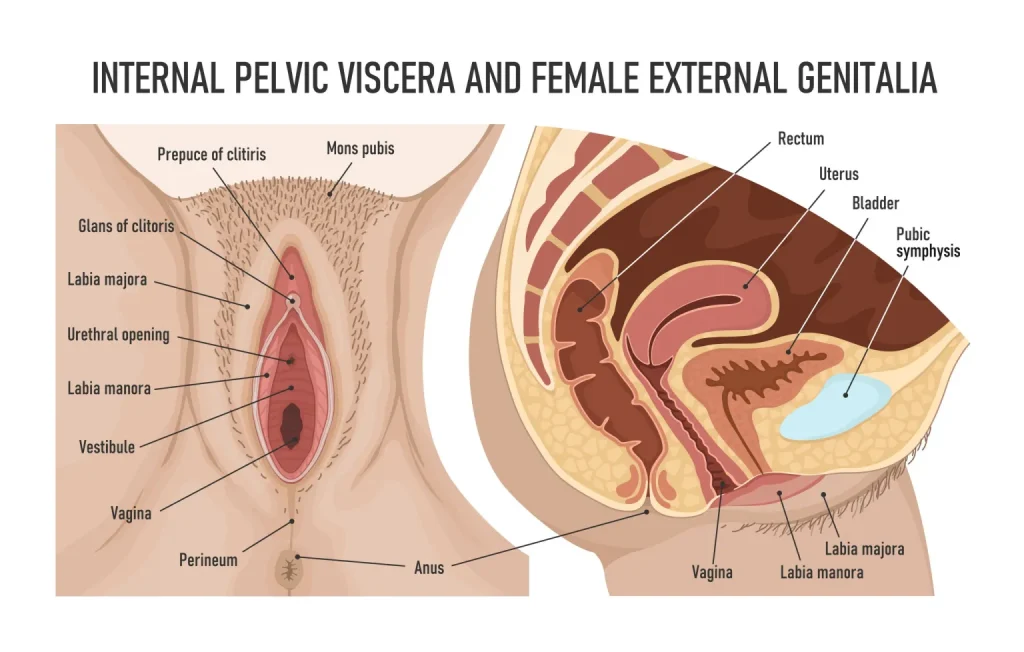
Outer Structure:
It is the main part of Viginal health the vigina is the exterior portion of the female genitalia, which consists of the clitoris, vulva entrance, and labia majora and minora (the outer and inner lips).
The hymen: A thin membrane that partially covers the love box opening in some women. Contrary to popular belief, the presence or absence of the hymen does not indicate virginity.
Internal Structure:
Vaginal walls:
The Viginal health vigina lined with smooth muscle tissue and mucous membranes. The walls of the vagina are elastic and capable of stretching to accommodate various activities such as sexual intercourse and childbirth.
Rugae:
The viginal walls feature folds known as rugae, which expand and contract to accommodate different sizes and shapes during sexual activity and childbirth.
G-spot:
The Gräfenberg spot, commonly referred to as the G-spot, is an erogenous zone located on the anterior wall of the vagina. Stimulation of the G-spot is believed to enhance sexual arousal and pleasure in some individuals.
Functions of the Vagina:
The vagina serves several essential functions beyond its role in sexual intercourse:
Sexual Pleasure:
The vagina is rich in nerve endings and sensitive tissues that contribute to sexual arousal and pleasure. It plays a central role in sexual activity by providing lubrication and accommodating penile penetration.
Childbirth:
During childbirth, the vagina serves as the birth canal through which the baby passes from the uterus to the outside world. Its elastic nature allows it to stretch to accommodate the baby’s head and body, facilitating a safe delivery.
Menstruation:
The vagina serves as the exit point for menstrual blood during menstruation. The menstrual flow passes through the cervix and into the vagina before exiting the body.
Natural Lubrication:
Thelove box walls produce mucus and lubricating fluids that help maintain moisture and pH balance, promoting vaginal cana health and comfort.
Maintaining Viginal Health:
Maintaining optimal vigina is essential for overall well-being and quality of life. Here are some tips for promotingit.
Practice Good Hygiene:
Clean the external genital area (vulva) regularly with mild soap and water. Avoid douching or using harsh cleansers, as these can disrupt the natural balance of vaginal flora and increase the risk of infection.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water to maintain adequate hydration, which helps keep vaginal tissues moist and healthy.
Safe Sex Practices:
Practice safe sex by using condoms or other barrier methods to prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Regular STI testing is also recommended, especially for individuals with multiple sexual partners.
Avoid Irritants:
Avoid using products that may irritate the vigina area, such as scented soaps, perfumes, or vaginal sprays. Opt for hypoallergenic and fragrance-free products whenever possible.
Regular Gynecological Exams:
Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider for pelvic exams and Pap smears to screen for cervical cancer and other gynecological conditions.
Conclusion:
The vaginal structure is a marvel of nature, encompassing a complex network of tissues and structures that contribute to sexual pleasure, childbirth, and overall viginal health. Understanding the anatomy and functions of the vagina is essential for promoting women’s health and well-being. By practicing good hygiene, safe sex, and regular gynecological care, individuals can maintain optimal viginal health and enjoy a fulfilling and healthy life.


