The human body is an intricately designed marvel, functioning like a well-orchestrated symphony where every part plays a crucial role. Among its many symphonic systems, the hormonal system stands out as a conductor, orchestrating various bodily functions and maintaining harmony within. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll embark on a journey through the complex world of hormones, exploring their role, regulation, and significance in maintaining optimal health.
Understanding the Hormonal System
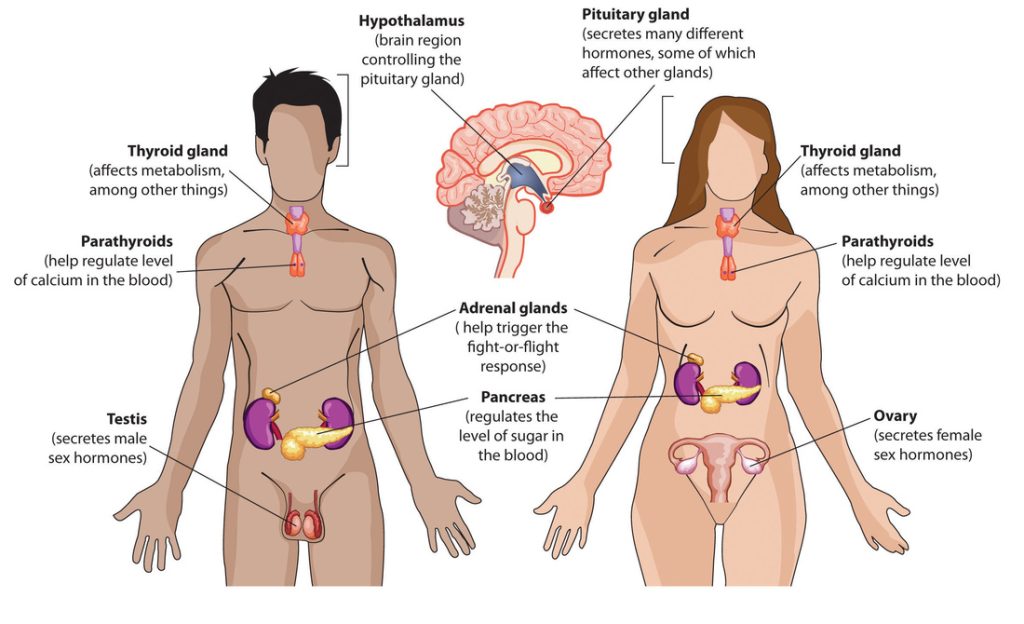
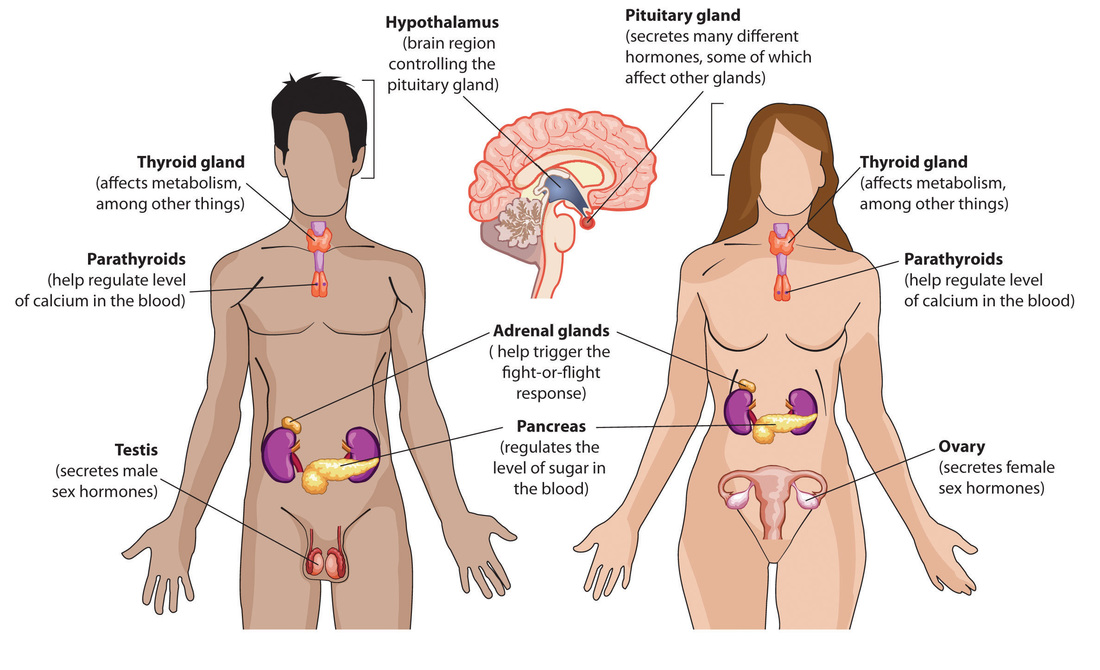
The hormonal system, also known as the endocrine system, comprises glands and organs that produce and release hormones—chemical messengers that regulate numerous physiological processes. These processes include metabolism, growth and development, reproduction, mood regulation, and stress response. Unlike the nervous system, which transmits messages via electrical signals, the hormonal system communicates through the bloodstream, reaching target cells and organs throughout the body.
The Key Players: Hormones and Glands
Several glands and organs make up the hormonal system, each secreting specific hormones with distinct functions:
Hypothalamus:
Situated in the brain, the hypothalamus acts as the master regulator of the hormonal system, producing hormones that stimulate or inhibit the release of hormones from the pituitary gland.
Pituitary Gland:
Often referred to as the “master gland,” the pituitary gland secretes a wide array of hormones that control other endocrine glands, including growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and follicle-stimulating hormone.
Thyroid Gland:
Located in the neck, the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy production, and body temperature, including thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
Adrenal Glands:
Positioned on top of the kidneys, the adrenal glands secrete hormones such as cortisol, adrenaline (epinephrine), and aldosterone, which regulate stress response, blood pressure, and electrolyte balance.
Pancreas:
The pancreas produces insulin and glucagon, hormones involved in regulating blood sugar levels and energy metabolism.
Gonads:
In males, the testes produce testosterone, which is essential for the development of male reproductive organs and secondary sexual characteristics. The female ovaries generate progesterone and estrogen, which help with pregnancy and menstrual cycle regulation.
Regulation of Hormonal Balance
Hormonal balance maintenance is essential for general health and well-being. However, hormonal imbalances can occur due to various factors, including genetics, aging, stress, diet, lifestyle, and environmental influences. Hormonal imbalances can manifest in a myriad of symptoms and health conditions, such as:
Thyroid Disorders:
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, characterized by underactive and overactive thyroid function, respectively, can lead to symptoms such as fatigue, weight changes, and mood disturbances.
Adrenal Dysfunction:
Conditions like Cushing’s syndrome and Addison’s disease result from abnormalities in adrenal hormone production, causing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain or loss, and electrolyte imbalances.
Reproductive Disorders:
Hormonal imbalances can disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to irregular periods, infertility, and symptoms like hot flashes, mood swings, and vaginal dryness during menopause.
Impact hormonal System
While some hormonal imbalances may stem from genetic predispositions or medical conditions, lifestyle factors play a significant role in maintaining hormonal balance:
Nutrition:
A balanced diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides essential nutrients that support hormonal function and metabolism.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise helps regulate hormones, improve insulin sensitivity, and reduce stress levels, contributing to overall hormonal balance and well-being.
Stress Management:
Chronic stress can disrupt hormonal balance by triggering the release of cortisol and adrenaline. Practices such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing, and mindfulness can help alleviate stress and promote hormonal harmony.
Sleep:
Adequate sleep is essential for hormonal regulation, as it allows the body to rest, repair, and recharge. Lack of sleep can disrupt hormone production, leading to imbalances and health problems.
Toxic Exposures:
Exposure to environmental toxins, chemicals, and endocrine-disrupting compounds found in pesticides, plastics, and personal care products can interfere with hormonal function and contribute to imbalances.
Hormonal Health and Aging
As we age, hormonal changes are a natural part of the aging process. For example, menopause in women and andropause in men are associated with declining levels of sex hormones, leading to symptoms such as hot flashes, mood swings, and decreased libido. While these changes are normal, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help mitigate their effects and support overall hormonal health as we age.
Seeking Balance and Harmony and hormonal system
Achieving hormonal balance is not a one-size-fits-all endeavour, as individual needs and circumstances vary. However, adopting a holistic approach to health and wellness can help support hormonal balance and promote


awesome