The human nervous system is a marvel of biological engineering, intricately designed to regulate every sensation, thought, and action we experience. Comprising a vast network of cells, it serves as the body’s command centre, coordinating responses to stimuli and maintaining homeostasis. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the complexities of the human nervous system, exploring its structure, function, and significance in our daily lives.
Understanding the Basics of The human nervous system
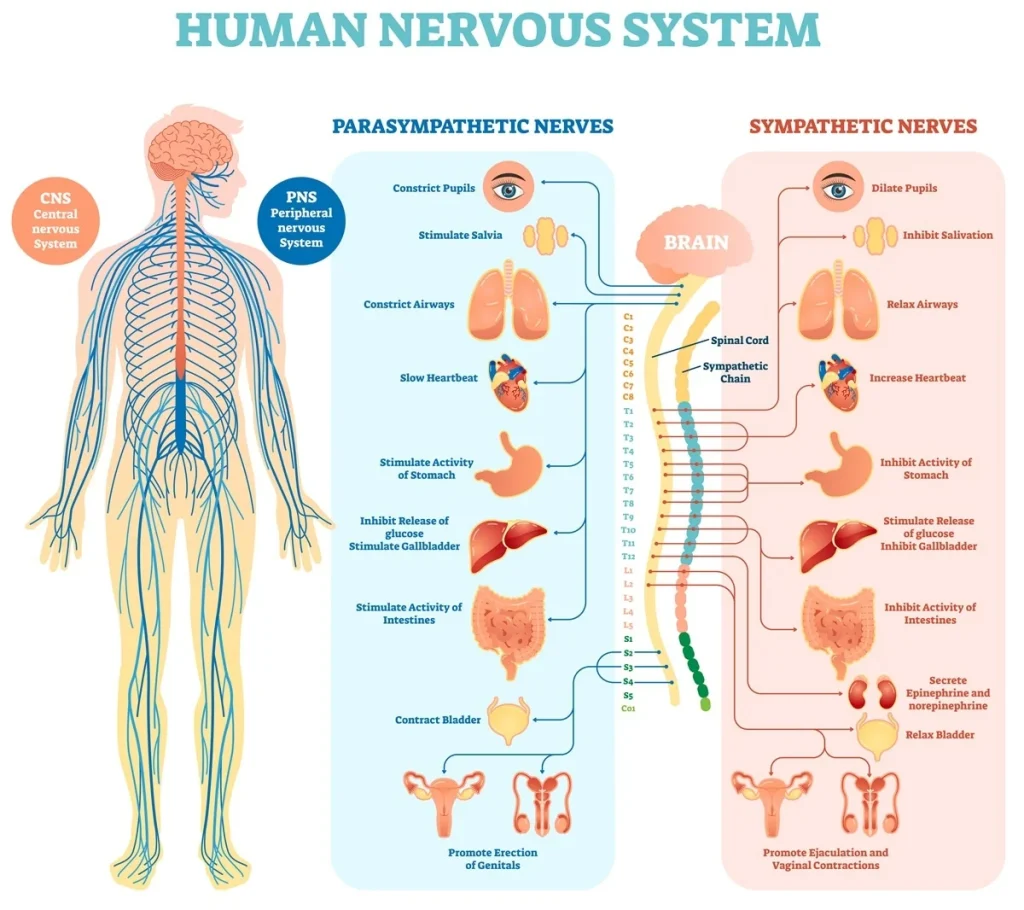
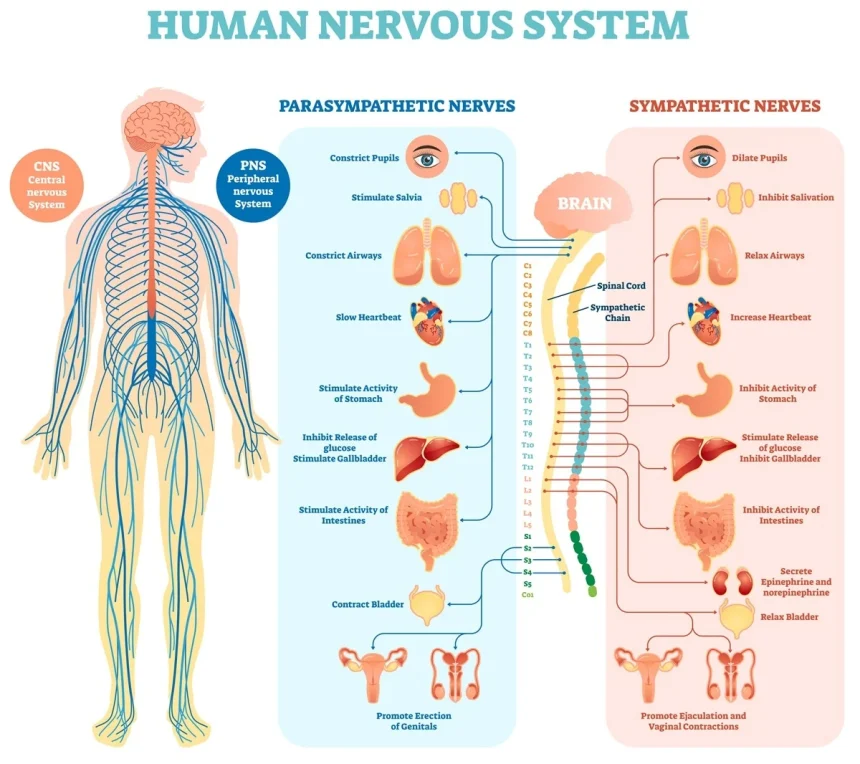
At its core, the nervous system is divided into two main components: the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS consists of the brain and spinal cord, while the PNS encompasses all nerves outside of this central structure. This division allows for efficient processing of information and communication between various parts of the body.
Structural Components:
The human nervous system is composed of billions of specialized cells called neurons, which transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body. These cells are interconnected through synapses, allowing for the transmission of information from one neuron to another.
Functionality:
The nervous system performs three basic functions sensory input, integration and motor outputSensory neurons gather information from sensory receptors and transmit it to the CNS. The brain then processes this information, integrating it with existing knowledge and generating appropriate responses. Finally, motor neurons convey signals from the CNS to muscles and glands, eliciting the necessary actions.
Subsystems:
Within the peripheral nervous system, there are further subdivisions, including the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system controls voluntary movements and sensory perception, while the autonomic nervous system regulates involuntary processes such as heart rate, digestion, and respiratory rate.
Brain: The Command Center:
As the most complex organ in the human body, the brain plays a central role in controlling all bodily functions. It is divided into several regions, each responsible for specific tasks such as motor control, sensory processing, memory, and emotion. The brain’s intricate network of neurons allows for the seamless integration of sensory information and the execution of precise motor responses.
Spinal Cord: The Information Highway:
Running from the base of the brain to the lower back, the spinal cord serves as a conduit for signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It also plays a crucial role in reflex actions, allowing for rapid responses to potential threats without the need for conscious processing.
Neurotransmitters: Chemical Messengers of The human nervous system
Communication between neurons occurs through the release of neurotransmitters, chemical substances that transmit signals across synapses. These neurotransmitters can have excitatory or inhibitory effects on the receiving neuron, influencing its likelihood of firing an action potential.
Disorders and Diseases of the Human Nervous System
A dysfunction in the nervous system can lead to a range of disorders and diseases, including neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. Additionally, mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and schizophrenia can arise from imbalances in neurotransmitter levels or structural abnormalities in the brain.
The Future of Neuroscience:
Advancements in neuroscience continue to expand our understanding of the human nervous system and its complexities. Technologies such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and optogenetics allow researchers to visualize brain activity and manipulate neural circuits with unprecedented precision. These innovations hold promise for the development of novel treatments for neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Conclusion:
The human nervous system is a marvel of biological evolution, enabling us to perceive the world around us, process information, and interact with our environment. From the intricate wiring of neurons to the elaborate functions of the brain, every aspect of this system is finely tuned to ensure our survival and well-being. As our understanding of neuroscience deepens, so too does our appreciation for the incredible complexity of the human mind and body.