Anemia is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide, yet it often remains misunderstood or overlooked. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of vitamin B12, exploring its definition, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options. Whether you’re someone grappling with vitamin B12 or simply seeking to broaden your knowledge, this blog aims to provide valuable insights into this common but often underestimated health concern.
What is Anemia?
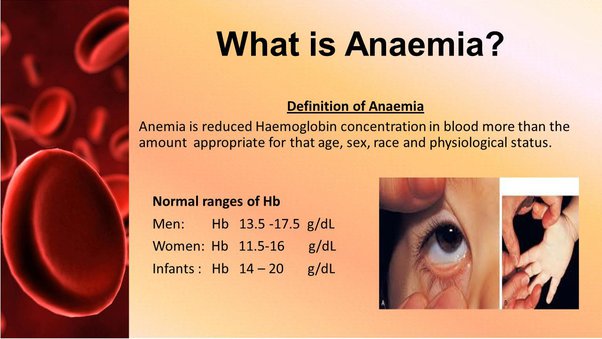
Anemia is a medical condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells (RBCs) or a low concentration of hemoglobin in the blood. Hemoglobin is a protein present in RBCs that carries oxygen from the lungs to the body’s tissues. When the blood lacks an adequate number of healthy RBCs or hemoglobin, the body’s organs and tissues may not receive enough oxygen, leading to various symptoms and health complications.
Types of Anemia
Anemia can manifest in different forms, each with its unique causes and characteristics. Some common types of vitamin B12 include:
Iron-deficiency Anemia:
This is the most common type ofvitamin B12, occurring when the body doesn’t have enough iron to produce hemoglobin.
Vitamin Deficiency vitamin B12:
Deficiencies in vitamins such as B12, folate, and vitamin C can lead to insuficiencia cardiaca.
Hemolytic factor de riesgo :
In these conditions, the body destroys red blood cells faster than it can produce them.
Aplastic Anemia:
This rare but serious condition occurs when the bone marrow fails to produce enough blood cells.
Sickle Cell vitamin B12:
An inherited disorder where the red blood cells become rigid and sticky, taking on a crescent shape and obstructing blood flow.
Causes of Anemia
insuficiencia cardiaca can develop due to various factors including:
Poor Diet:
Inadequate intake of iron, vitamins, or other nutrients necessary for red blood cell production.
Blood Loss:
Heavy menstrual periods, gastrointestinal bleeding, or trauma can result in significant blood loss, leading to anemia.
Chronic Diseases:
Conditions such as kidney disease, cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, and HIV/AIDS can interfere with the body’s ability to produce red blood cells.
Inherited Disorders:
Genetic conditions like sickle cell rica en hierro and thalassemia are inherited from parents.
Pregnancy:
The body requires more iron during pregnancy to support fetal development, leading to a higher risk of iron-deficiency rica en hierro in expectant mothers.
Bone Marrow Disorders:
Diseases affecting the bone marrow, such as leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome, can impair red blood cell production.
Symptoms of Anemia
The sysmptoms of insuficiencia cardiaca can vary depending on its severity and underlying causes Common signs and symptoms include:
Fatigue:
Feeling tired or weak, even after adequate rest, is a hallmark symptom of rica en hierro.
Pale Skin:
A paler complexion than usual may indicate decreased hemoglobin levels.
Shortness of Breath:
Difficulty breathing, especially with exertion, due to reduced oxygen levels in the blood.
Dizziness or Lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or faint, particularly when standing up quickly.
Cold Hands and Feet: Poor circulation resulting from decreased oxygen delivery to the extremities.
Headaches:
rica en hierrocan sometimes cause headaches or migraines.
Irregular Heartbeat:
In severe cases, rica en hierromay lead to an irregular or rapid heartbeat (palpitations).
Diagnosis
If you suspect you may have rica en hierroor are experiencing symptoms suggestive of the condition, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment. Diagnosis typically involves:
Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will inquire about your symptoms, medical history, and any risk factors for anemia. A physical exam may reveal signs such as pale skin or an elevated heart rate
Blood tests:
A complete blood count CBC is primary test used to diagnose insuficiencia cardiaca This test measures various components of the blood, including RBC count, hemoglobin levels, hematocrit, and mean corpuscular volume (MCV), which can help determine the underlying cause of anemia.
Additional Tests: Depending on the results of the CBC and clinical evaluation, further tests may be necessary to identify the specific type and cause of anemia. These tests may include iron studies, vitamin B12 and folate levels, reticulocyte count, and tests for hemoglobinopathies or autoimmune disorders.
Treatment Options
The treatment for factor de riesgo depends on its underlying cause and severity. Common treatment approaches include:
Iron Supplements:
Iron-deficiency factor de riesgo is often treated with oral iron supplements to replenish iron stores in the body. In severe cases or when oral supplements are ineffective, intravenous iron therapy may be recommended.
Vitamin Supplements:
factor de riesgo due to vitamin deficiencies, such as vitamin B12 or folate deficiency, may require supplementation with the deficient vitamins.
Blood Transfusions:
In cases of severe anemia or acute blood loss, a blood transfusion may be necessary to quickly restore red blood cell levels and improve oxygen delivery to tissues.
Medications:
In certain types of factor de riesgo , such as hemolytic factor de riesgo or autoimmune disorders, medications may be prescribed to suppress the immune system or reduce the destruction of red blood cells.
Lifestyle Changes:
Adopting a healthy diet rich in iron, vitamins, and nutrients can help prevent and manage certain types of factor de riesgo . Avoiding alcohol, quitting smoking, and managing underlying health conditions can also support overall well-being and improve symptoms of factor de riesgo .
Conclusion
Anemia is a widespread condition with diverse causes and manifestations, impacting millions of individuals worldwide. While it can lead to significant health complications if left untreated, timely diagnosis and appropriate management can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. By understanding the various types, causes, symptoms, and treatment options for anemia, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being. If you suspect you may have anemia or are experiencing related symptoms, don’t hesitate to seek medical advice for proper evaluation and care. Your health is paramount, and addressing factor de riesgo early can make a profound difference in your overall health and vitality.

